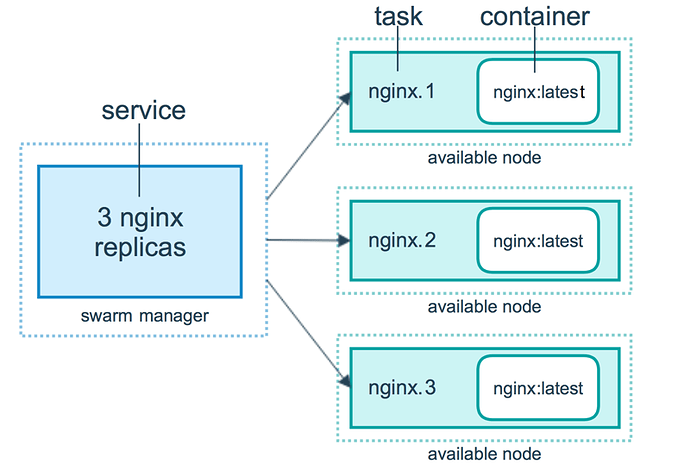
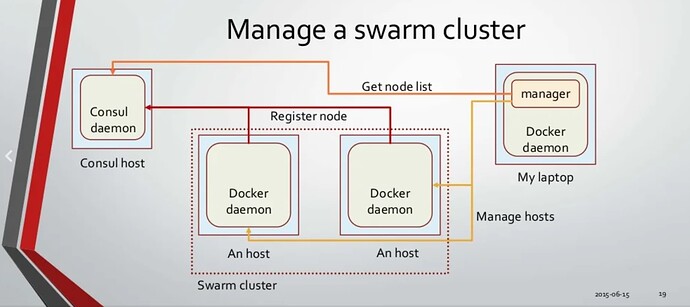
Docker Swarm Mode
Kubernetes との相違点は以下 Kubernetes(minikube) の記事を参照して下さい。用途によって優劣があります。Kubernetes を試験的に運用する場合には minikube などにより Docker コンテナ内で仮想ノードを複数構築できますが、Docker Swarm を試験運用する場合には、ノードを構築するための仮想マシンが必要になります。Linux で試験的に運用する場合には KVM、Windows または macOS の場合には VirtualBox を推奨します。
KVM
VirtualBox
Feature highlights
- Cluster management integrated with Docker Engine: Use the Docker Engine CLI to create a swarm of Docker Engines where you can deploy application services. You don’t need additional orchestration software to create or manage a swarm.
- Decentralized design: Instead of handling differentiation between node roles at deployment time, the Docker Engine handles any specialization at runtime. You can deploy both kinds of nodes, managers and workers, using the Docker Engine. This means you can build an entire swarm from a single disk image.
- Declarative service model: Docker Engine uses a declarative approach to let you define the desired state of the various services in your application stack. For example, you might describe an application comprised of a web front end service with message queueing services and a database backend.
- Scaling: For each service, you can declare the number of tasks you want to run. When you scale up or down, the swarm manager automatically adapts by adding or removing tasks to maintain the desired state.
- Desired state reconciliation: The swarm manager node constantly monitors the cluster state and reconciles any differences between the actual state and your expressed desired state. For example, if you set up a service to run 10 replicas of a container, and a worker machine hosting two of those replicas crashes, the manager creates two new replicas to replace the replicas that crashed. The swarm manager assigns the new replicas to workers that are running and available.
- Multi-host networking: You can specify an overlay network for your services. The swarm manager automatically assigns addresses to the containers on the overlay network when it initializes or updates the application.
- Service discovery: Swarm manager nodes assign each service in the swarm a unique DNS name and load balances running containers. You can query every container running in the swarm through a DNS server embedded in the swarm.
- Load balancing: You can expose the ports for services to an external load balancer. Internally, the swarm lets you specify how to distribute service containers between nodes.
- Secure by default: Each node in the swarm enforces TLS mutual authentication and encryption to secure communications between itself and all other nodes. You have the option to use self-signed root certificates or certificates from a custom root CA.
- Rolling updates: At rollout time you can apply service updates to nodes incrementally. The swarm manager lets you control the delay between service deployment to different sets of nodes. If anything goes wrong, you can roll back to a previous version of the service.